This blog post aims at breaking down the very common concepts in cloud computing. To start off, what is cloud computing?
Cloud Computing Defined
Cloud computing is the delivery of on-demand computing services -- which includes data storage, servers, databases, networking, and software -- typically over the internet and on a pay-as-you-go basis. It is the provision of services such as infrastructure, platform or software over the internet.
Instead of buying, owning, and maintaining physical data centers and servers, you can access technology services, such as computing power, storage, and databases, on an as-needed basis from a cloud provider. These resources are owned and managed by a third-party provider, instead of the end-user.
Simply put , It means storing and accessing data over the Internet.
The traditional process of maintaining and storing data in physical data centers has a lot of limitation varying from power supply, labor, capital, expertise all the way to maintenance. Cloud computing has made this process simpler and easier.
Platforms that provide cloud computing services include:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud
- IBM Cloud
- Oracle Cloud
- SAP and many others.
Types of Cloud Computing Services
Cloud computing services are delivered in three main models, each of which offers customers different levels of support and flexibility. These services are occasionally known as the cloud computing ‘stack’ as they are often built on top of one another.
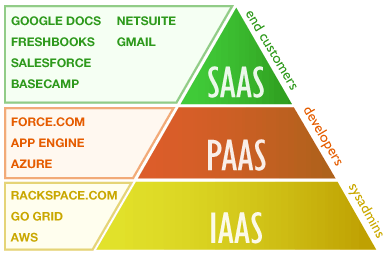
SAAS (Software-as-a-Service)
SaaS(Software as a Service) is a software solution delivered as service over the internet on a pay-as-you-go basis. It provides clients with the ability to use software applications remotely via an internet web browser without having to download or maintain any software. The public cloud provider manages all the hardware and traditional software, including middleware, application software, and security. So SaaS customers can lower costs, deploy, scale, and upgrade business solutions more quickly than maintaining on-premises systems and software; and predict total cost of ownership with greater accuracy.
Examples of SaaS applications include any web-based mail services. The different services supplied by Google such as Google Docs and Google Sheets are also examples of SaaS. Adobe Creative Cloud services is also another example of SaaS in action. With this kind of model, the user is only exposed to the interface that they choose to interact with.
PAAS (Platform-as-a-Service)
PaaS provides platform infrastructure to build, test and deploy software. PaaS is considered the most complex of the three layers of cloud-based computing. PaaS shares some similarities with SaaS, the primary difference being that instead of delivering software online, it is actually a platform for creating software that is delivered via the Internet. Examples include AWS RDS, Google App Engine, AWS Elastic Beanstalk. It’s effectively an option to develop an application without having to worry about installing, configuring, and maintaining an infrastructure. This is supplied by the server as a standardized environment.
IAAS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service)
This is the on-demand delivery of computing infrastructure. It provides virtual computing infrastructure which is provisioned, managed and maintained. IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) allows clients to remotely use IT hardware and resources on a "pay-as-you-go" basis. It is also referred to as HaaS(Hardware as a service). The simplest example of IaaS cloud computing is ordinary web-hosting. This is where you pay a monthly fee or by megabyte/gigabyte to have a company host your files from their servers. IaaS is an extremely flexible option, as it permits the user to customize the infrastructure of the computing environment.
Cloud Computing Deployment Models
Cloud deployment model describes how cloud computing platform is implemented and how it is hosted and who has access to the platform.
Public Cloud
It has a massive amount of computing and storage resources, it is easily scalable, flexible and accessible. Public cloud environments are operated by third-party/cloud providers. They provide computing resources such as servers and storage options using the Internet. The cloud provider hosts the cloud infrastructure, and end users can access it remotely without the need to buy and set up a working environment (such as buying hardware and software). Public cloud resources are shared among different end users. Users are typically charged for the duration for which these services are used (pay-as-you-go). This is the recommended choice for developing cloud based application for globally distributed teams.
Private Cloud
In a private cloud, the cloud infrastructure is owned by a single business or organization. It is restrictive, has tighter control and is protected by a firewall. It is called an on-premises cloud solution. This means that only the company's employees can have access to this cloud system. Private clouds are more expensive than public clouds due to the capital expenditure involved in acquiring and maintaining them.
Hybrid Cloud
It combines both public and private clouds. It allows seamless interaction between public and private clouds. For example, public clouds can access data and applications of private clouds and the converse is also possible. Private clouds are more expensive than public clouds due to the capital expenditure involved in acquiring and maintaining them.
Community Cloud
This deployment model is collaborative and multitenant in nature, usually catered for the same type of businesses or industries which share the exact requirements in terms of security and compliance. It is not commonly used as the other three models.
Advantages of Cloud Computing

Scalability
Cloud computing has been developed to scale quickly and handle unexpected growth, depending on the level of traffic your website receives.
Pay-as-you-use
This means that you have an upfront cost of how much you think you use, which you can then adjust as and when you need to. If you haven’t used as much storage as you thought you needed, it’s very easy to downscale.
Accessibility
Cloud computing is far more than just accessing files on multiple devices. Thanks to cloud computing services, users can check their email on any computer and even store files using services such as Dropbox and Google Drive. Cloud computing services also make it possible for users to back up their music, files, and photos, ensuring those files are immediately available in the event of a hard drive crash.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
Downtime
The cloud, like any other IT set up, can experience technical problems such as reboots, network outages and downtime. These events can incapacitate business operations and processes, and can be damaging to business.
Security
While regulations force cloud computing services to shore up their security and compliance measures, it remains an ongoing issue. Encryption protects vital information, but if that encryption key is lost, the data disappears. These risks can come from both potential attackers as well as the fact that you are trusting a third party in an unknown location with potentially sensitive and private information.
Vendor lock-in
This is the condition where it becomes difficult, or occasionally impossible, to change cloud computing service vendors due to the computing systems you have in place being closed and proprietary. Migrating to a different cloud computing server is tricky in itself, but having too much of a structure in your current system can make it even harder.
